The problem
Single-use plastics, or disposable plastics, are used only once before they are thrown away or recycled. These items are things like plastic bags, straws, coffee stirrers, soda and water bottles and most food packaging.
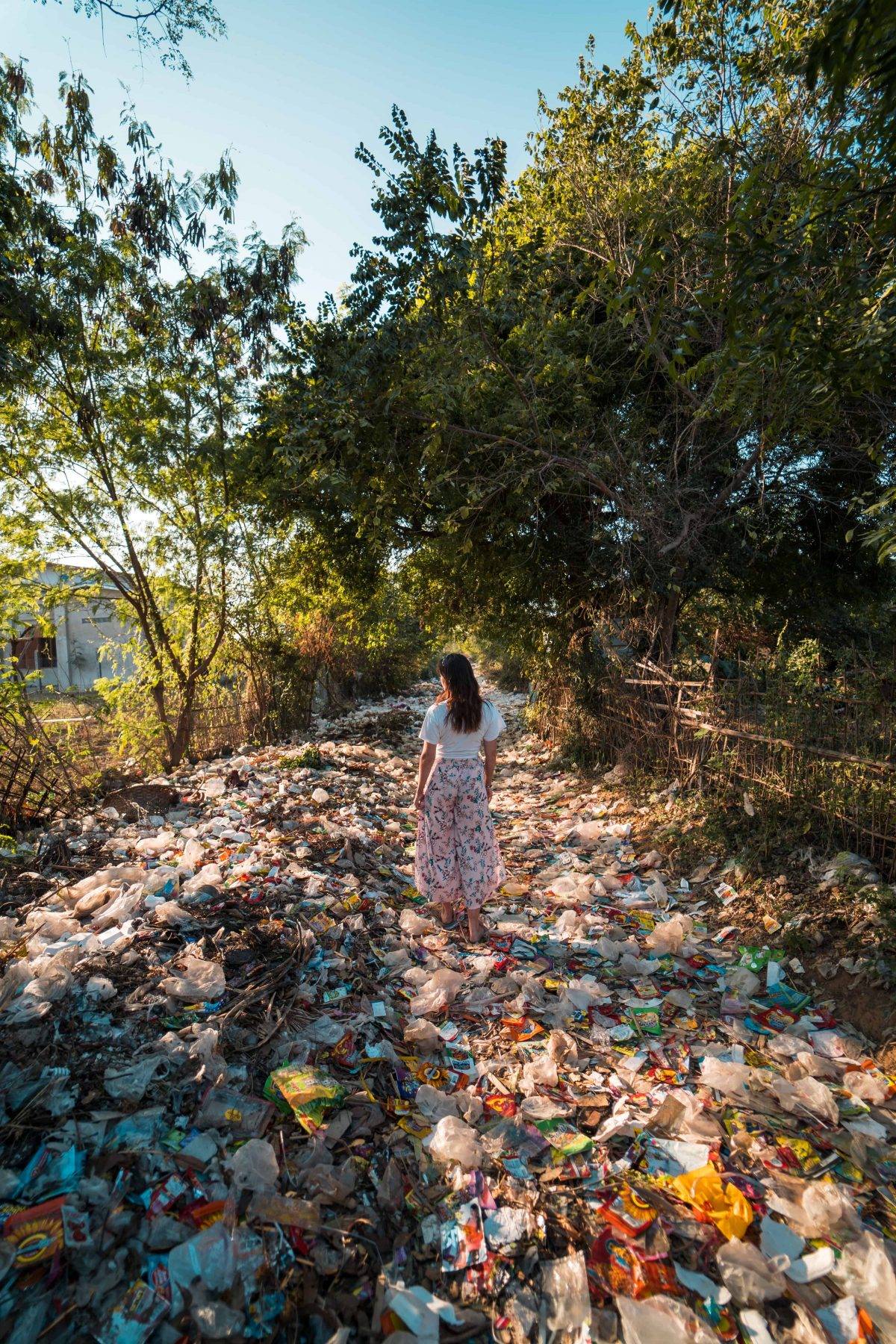
We produce roughly 300 million tons of plastic each year and half of it is disposable! World-wide only 10-13% of plastic items are recycled. The nature of petroleum based disposable plastic makes it difficult to recycle and they have to add new virgin materials and chemicals to it to do so. Additionally there are a limited number of items that recycled plastic can be used.
Petroleum based plastic is not biodegradable and usually goes into a landfill where it is buried or it gets into the water and finds its way into the ocean. Although plastic will not biodegrade (decompose into natural substance like soil,) it will degrade (break down) into tiny particles after many years. In the process of breaking down, it releases toxic chemicals (additives that were used to shape and harden the plastic) which make their way into our food and water supply.
These toxic chemicals are now being found in our bloodstream and the latest research has found them to disrupt the Endocrine system which can cause cancer, infertility, birth defects, impaired immunity and many other ailments.
We produce hundreds of millions of tons of plastic every year, most of which cannot be recycled. It’s obvious that we need to use less plastic, move towards environmentally sustainable products and services and come up with technology that recycles plastic more efficiently.
Indian case
There are few materials as versatile as plastic, most of which is made from oil, natural gas and coal. It makes packaged foods last longer on store shelves and withstand extreme temperatures while being transported. Packaging accounts for a third of India’s plastic consumption. And 70 per cent of plastic packaging is turned into waste in a short span, as per a report by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
India generated 26,000 tonnes per day (TPD) of plastic waste in 2017-18, the latest year for which data is available, according to the Central Pollution Control Board. Of that, 15,600 TPD, or 60 per cent , was recycled. The rest ended up as litter on roads, in landfills or in streams. Uncollected plastic waste poses a huge threat to species on land and in water.
Around eight million tonnes of plastic waste enter the ocean every year. The river Ganga alone took 1.15 lakh tonnes of plastic into the ocean in 2015, second only to China’s Yangtze, according to a research paper published in Nature Communications magazine.
India’s plastic recycling rate is 60 per cent , three times higher than the global average of 20 per cent , and India’s per capita plastic consumption — at 11 kg in 2014-15 — is less than half the global average of 28 kg. In 2016, India said it wanted to increase the per capita plastic use to 20 kg by 2022. Since half the plastic now produced is meant to be used only once, India has to figure out what plastic it wants to use and ban — and how it will recycle all that trash.
Economic dimension
India’s plastic-processing industry has over 30,000 units and an annual turnover of Rs 2.25 lakh crore, according to the All India Plastic Manufacturers’ Association (AIPMA). The industry also employs over 4 million people. The government will have to carefully weigh the impact of a ban, in terms of plant closures and job losses, at a time of economic downturn.
Even if the government chooses to ban certain plastics, there is a big question mark on how effective it will be. Plastic is cheap and convenient, and as long as there is demand for it, people are going to manufacture it.
A ban would most likely target plastic cutlery, straws, cups and glasses, which, are mostly made by the unorganized segment. Union food and consumer affairs ministry , recently announced that plastic bottles for water will stay till an affordable alternative is found. But there have been reports that the government could put an end to 200 ml water bottles.
Way forward
Faced with increasing amounts of waste, government, have reviewed available policy options and concluded that placing the responsibility for the post-consumer phase of certain goods on producers could be an option. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is a policy approach under which producers are given a significant responsibility – financial and/or physical – for the treatment or disposal of post-consumer products. Assigning such responsibility could in principle provide incentives to prevent wastes at the source, promote product design for the environment and support the achievement of public recycling and materials management goals.